Exploring the Benefits of Pea and Lentil Proteins: A Sustainable Alternative
Alternative proteins have become increasingly popular in recent years as consumers seek healthier and more sustainable food options. Pea and lentil proteins stand out for their nutritional benefits and versatility. This article delves into the advantages of incorporating pea and lentil proteins into your diet, explaining why these plant-based powerhouses are gaining traction in the food industry.
What Are Pea and Lentil Proteins?
Pea protein is derived from yellow peas, while lentil protein comes from the seeds of the lentil plant. Both are excellent plant-based protein sources, offering a sustainable and nutritious alternative to animal proteins. These proteins are extracted by isolating the protein content, making it highly concentrated and beneficial for various dietary needs.
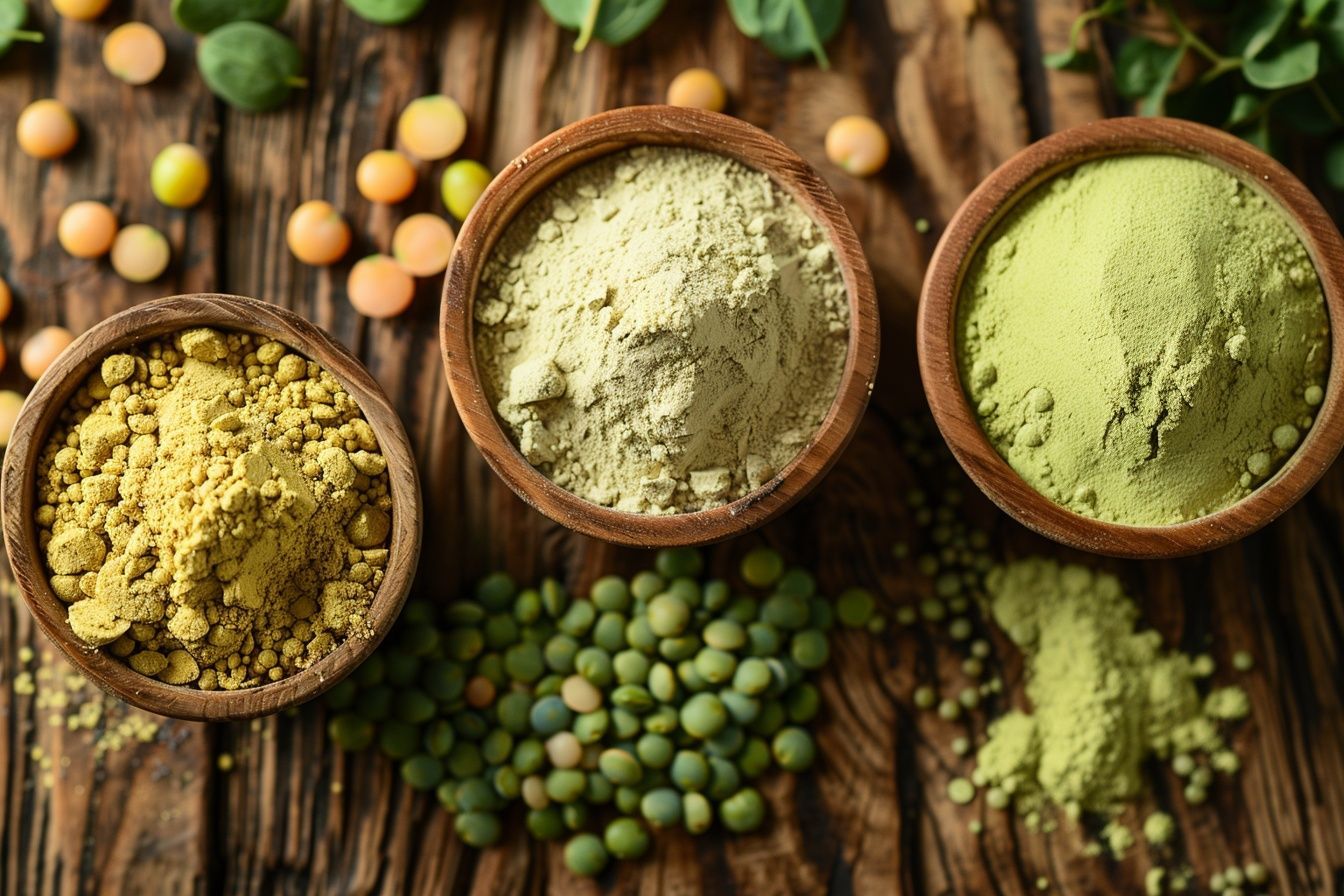

Nutritional Benefits of Pea and Lentil Proteins
Pea and lentil proteins are rich in essential amino acids, the building blocks of protein our bodies need but cannot produce independently. This makes them a complete protein source, particularly pea protein, comparable to animal proteins in their amino acid profile. Lentil protein is also highly nutritious, providing a good balance of essential amino acids.
Both proteins are low in fat and contain no cholesterol, making them heart-healthy options. They are also high in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. Moreover, pea and lentil proteins are hypoallergenic, meaning they are suitable for people with common food allergies, including those allergic to soy or dairy.
Incorporating Pea and Lentil Proteins into Your Diet
Adding pea and lentil proteins to your diet is easy and beneficial. Look for products that list pea or lentil protein as a primary ingredient, such as protein powders, plant-based meats, and protein-fortified snacks. You can also experiment with cooking dried peas and lentils in soups, stews, and salads for a nutritious boost.

Environmental Impact of Pea and Lentil Proteins
One of the most compelling reasons to choose pea and lentil proteins is their positive environmental impact. Producing these plant-based proteins requires significantly less water and land than animal protein production. Additionally, peas and lentils are nitrogen-fixing crops, which means they naturally replenish soil nutrients, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Versatility in Food Applications
Pea and lentil proteins are incredibly versatile and can be incorporated into a wide range of foods. They can be used to create meat substitutes, dairy-free products, protein bars, and even baked goods. Their neutral flavor makes them an excellent ingredient in various recipes, from smoothies to savory dishes.
Conclusion
Pea and lentil proteins offer a multitude of health benefits and contribute to a more sustainable food system. As awareness of these alternative proteins grows, more people turn to these plant-based options to support their health and the environment. Whether you want to enhance your diet or reduce your ecological footprint, pea and lentil proteins are an excellent choice.
By understanding the advantages of pea and lentil proteins, you can make informed decisions that benefit your well-being and the planet.

Join Our Newsletter
And be advised when new content is coming up
News Letter